Product Description
|
|
|
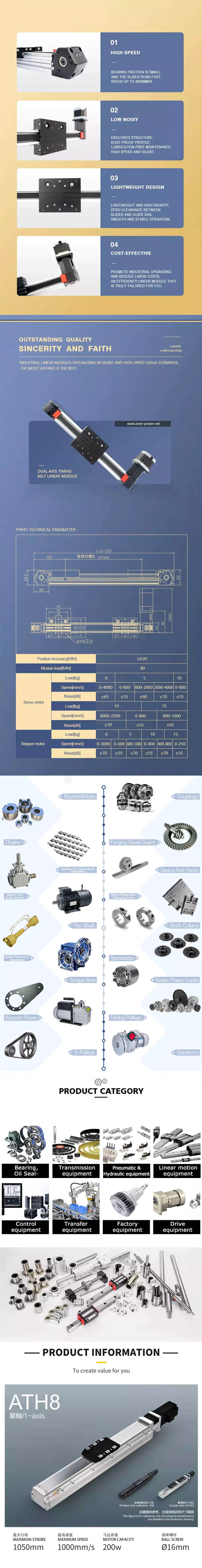
| X-axis (CFG8) Position repeatability: ±0.01(mm) Ball screw lead: 20(mm) Maximum speed:1000(mm/sec) Standard effective stroke: 50~1100(mm) Suitable motor capacity: servo 200W |
|
CF Seiko is a leading manufacturer of linear modules in China, dedicated to advancing industrial automation since our establishment in 2004. We set high standards and deliver top-quality products from our 2 factories in China, covering an area of 9000 square CHINAMFG ., with a team of 150 highly skilled technicians and engineers.
At CF Seiko, we specialize in designing and manufacturing linear modules and have established strong partnerships with over 20 listed companies, including industry giants such as FOXCONN, BYD, GREE, BOE, and more.
Our products offer the same quality as renowned brands like HIWIN, THK, IAI,Misumi and SMC, but at a much more competitive price. We prioritize quality and do not compromise on product standards. We also OEM for these brands.
Our product range includes:
1. Linear Motors
2. Electric Servo Cylinders
3. Ball Screw Linear Modules
4. Belt Driven Linear Modules
5. Rack and Pinion Linear Modules
6. Electric Cylinders Rod Type
7. Cartesian Robots
8. KK Series Module
We are currently seeking distributors in your country. By partnering with us, you can enjoy special discounts, high profits, guaranteed quality, and excellent after-sales service. Our diverse product line is designed to meet all your needs. Join us and explore new opportunities for wealth and success.
If you are interested in becoming a distributor for CF Seiko or would like more information, please do not hesitate to contact us. We are excited about the prospect of collaborating with you to expand our presence in your market.
Thank you for considering CF Seiko as a potential partner.
Warm regards,
Morty Lv(Foreign Trade Director)
FAQ
01HOW TO CONTROL THE PRODUCTS QUALITY?
Combining advanced equipment and strict management, we provide high standard and quality bearings for our customers all over the world.
02 WHAT IS THE TRANSPORTATION?
If small quantity, we suggest to send by express, such as DHL,UPS, TNT FEDEX. If large amount ,by air or sea shipping.
03 Can you offer OEM services?
Yes, we provide OEM service. Which means size, quantity, design, packing solution, etc. we will depend on your requests; and your logo will be customized on our products.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | Life Cycle |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 10.000 Hours |
| Muscle Size: | 1~11kg |
| Certification: | ISO |
| Control Mode: | Continuous Path Control |
| Drive Mode: | Electric |
| Customization: |
Available
|
|
|---|
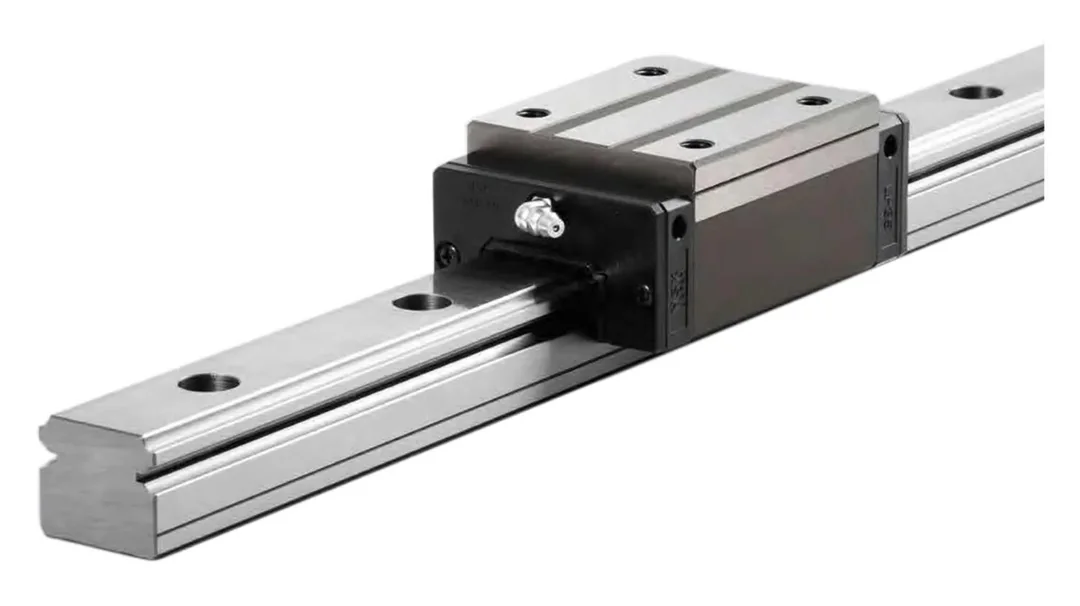

Can you describe the various mounting options and installations for linear rails in different settings?
Linear rails can be mounted in various configurations to suit different settings and applications. The choice of mounting options depends on factors such as space constraints, load requirements, and the desired motion characteristics. Here are some common mounting options and installations:
1. Horizontal Mounting: Linear rails are horizontally mounted when the desired linear motion is along the horizontal axis. This configuration is commonly used in applications such as CNC machines, where the tool needs to move horizontally across the workpiece.
2. Vertical Mounting: Vertical mounting involves installing linear rails to support vertical linear motion. This configuration is prevalent in applications like vertical machining centers, where the spindle moves vertically to perform machining operations on the workpiece.
3. Inverted Mounting: Inverted mounting is where the linear rail is installed upside down. This configuration is suitable when space limitations or specific design requirements dictate the need for the rail to be positioned below the moving component. Inverted mounting is common in some types of robotic systems.
4. Parallel Mounting: Linear rails can be mounted in parallel to support multiple carriages or moving components. This configuration is beneficial in applications where synchronized linear motion is required, such as in certain types of material handling systems or conveyor belts.
5. Cantilever Mounting: Cantilever mounting involves mounting the linear rail with one end extending beyond a support structure. This configuration is used when access to one side of the linear motion is required, such as in loading and unloading stations on manufacturing lines.
6. Tandem Mounting: Tandem mounting involves mounting multiple linear rails in tandem to share the load and provide additional support. This configuration is suitable for applications with heavy loads or long travel distances, ensuring stability and preventing deflection.
7. Floating Mounting: Floating mounting allows for some degree of flexibility in the alignment of the linear rail. This is useful in applications where there may be minor misalignments or variations in the mounting surface.
The choice of mounting option depends on the specific requirements of the application, and engineers must carefully consider factors such as load distribution, accessibility, and alignment to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the linear rail system.
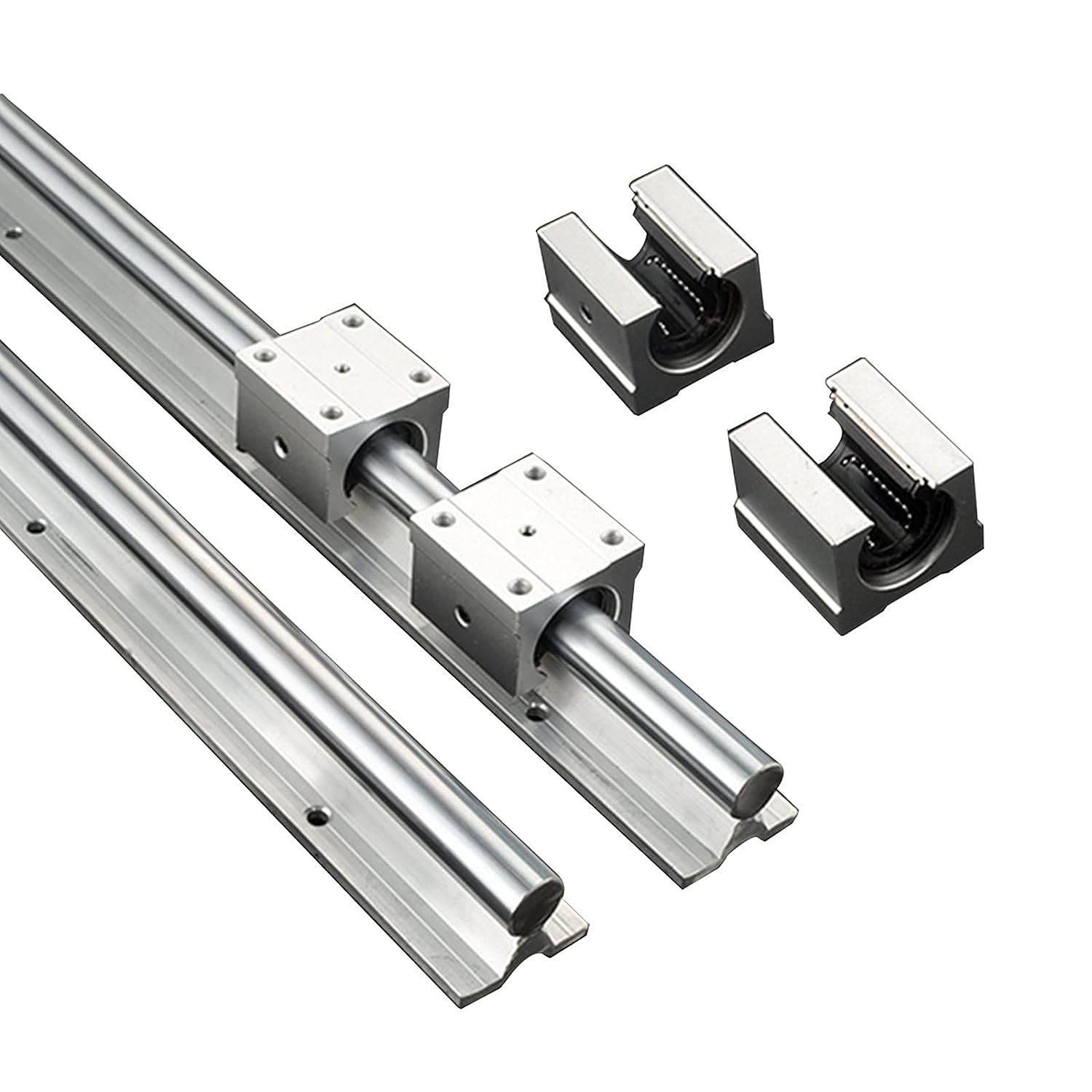

How do innovations and advancements in linear rail technology impact their use?
Innovations and advancements in linear rail technology have a profound impact on their use, influencing performance, efficiency, and application possibilities. Here are key ways in which technological advancements impact the use of linear rails:
- 1. Enhanced Precision: Advancements in manufacturing processes and materials contribute to higher precision in the design and production of linear rails. This results in improved accuracy and repeatability in linear motion applications, making them suitable for tasks requiring intricate and precise movements, such as in CNC machining and 3D printing.
- 2. Increased Load Capacities: Ongoing innovations allow for the development of linear rails with increased load-bearing capabilities. This is particularly beneficial in industries and applications where heavy loads need to be moved with precision, such as in industrial automation and material handling systems.
- 3. Integration of Smart Technologies: The integration of smart technologies, such as sensors and feedback systems, enhances the monitoring and control capabilities of linear rail systems. This facilitates real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and improved overall system efficiency, particularly in automated and Industry 4.0 settings.
- 4. Energy Efficiency: Innovations in lubrication systems and materials contribute to increased energy efficiency in linear rail operation. Reduced friction and optimized designs help minimize energy consumption, making linear rails more environmentally friendly and cost-effective over their lifespan.
- 5. Customization and Modularity: Advanced manufacturing techniques enable greater customization and modularity in linear rail systems. Engineers can tailor linear rails to specific application needs, adjusting parameters such as length, load capacity, and material composition for optimal performance in diverse industrial and automation scenarios.
- 6. Durability and Longevity: Continuous improvements in materials and surface treatments enhance the durability and longevity of linear rails. This is particularly beneficial in applications where reliability and minimal maintenance are critical, such as in aerospace testing equipment and high-precision manufacturing.
Overall, innovations in linear rail technology contribute to a broader range of applications, improved performance metrics, and the ability to meet the evolving needs of diverse industries. As technology continues to advance, the versatility and effectiveness of linear rails in various industrial and automation settings are likely to expand even further.

What are linear rails, and how are they used in linear motion systems?
Linear rails, also known as linear guides or linear slides, are mechanical components used in linear motion systems to facilitate smooth and precise movement along a straight path. They typically consist of a rail and a carriage. The rail is a long, rigid structure with a specially designed profile, while the carriage is mounted on the rail and holds the load to be moved.
Linear rails are widely used in various applications, including manufacturing machinery, robotics, 3D printers, and automated systems. They provide guidance and support to the moving components, minimizing friction and ensuring accurate and repeatable motion. The design of linear rails allows for high load-carrying capacity and can accommodate different types of loads, such as radial or axial loads.
Linear motion systems incorporating linear rails offer advantages such as improved precision, reduced wear and tear, and increased efficiency in comparison to traditional sliding mechanisms. The choice of linear rails depends on factors such as load capacity, speed, accuracy requirements, and environmental conditions in the specific application.

editor by Dream 2024-05-16